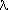 x for some scalar
x for some scalar 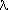 .
.
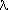 is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial solution
x of Ax =
is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial solution
x of Ax = 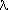 x. In this case x is the eigenvector
corresponding to
x. In this case x is the eigenvector
corresponding to 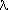 . (A "nontrivial" solution vector x is a vector that has at least
one nonzero entry.)
. (A "nontrivial" solution vector x is a vector that has at least
one nonzero entry.)
| eigenvector |
An eigenvector of an nxn matrix A is a nonzero vector x such that Ax =
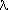 x for some scalar x for some scalar 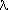 . .
|
| eigenvalue |
A scalar 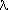 is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial solution
x of Ax = is called an eigenvalue of A if there is a nontrivial solution
x of Ax = 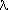 x. In this case x is the eigenvector
corresponding to x. In this case x is the eigenvector
corresponding to 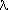 . (A "nontrivial" solution vector x is a vector that has at least
one nonzero entry.) . (A "nontrivial" solution vector x is a vector that has at least
one nonzero entry.)
|
The symbol 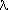 is the lowercase Greek letter Lambda and is frequently used to denote eigenvalues.
is the lowercase Greek letter Lambda and is frequently used to denote eigenvalues.
The equation Ax = 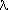 x is called the eigenvalue-eigenvector equation.
Notice that x = 0 always satisfies this equation, which is why it is called the trivial solution. However, we never consider x = 0
to be an eigenvector. Reasons for this include the fact that 0 is linearly dependent with any set of vectors from Rn and also
that it would allow any scalar to be considered an eigenvalue.
x is called the eigenvalue-eigenvector equation.
Notice that x = 0 always satisfies this equation, which is why it is called the trivial solution. However, we never consider x = 0
to be an eigenvector. Reasons for this include the fact that 0 is linearly dependent with any set of vectors from Rn and also
that it would allow any scalar to be considered an eigenvalue.
 |